Estonia curriculum success
Estonia’s Curriculum Success A Model for Modern Education Reform
Estonia’s education system has garnered global acclaim for its remarkable success in improving student outcomes, fostering innovation, and closing achievement gaps in a relatively short period. At the heart of this transformation lies a carefully crafted curriculum that reflects Estonia’s commitment to high quality education, equity, and adaptability in a rapidly changing world. Estonia’s curriculum success is not accidental but the result of strategic policymaking, sustained investment, and a culture that values lifelong learning and critical thinking. Exploring the elements that underpin Estonia’s curriculum offers valuable insights into how a small country can become an international leader in education.
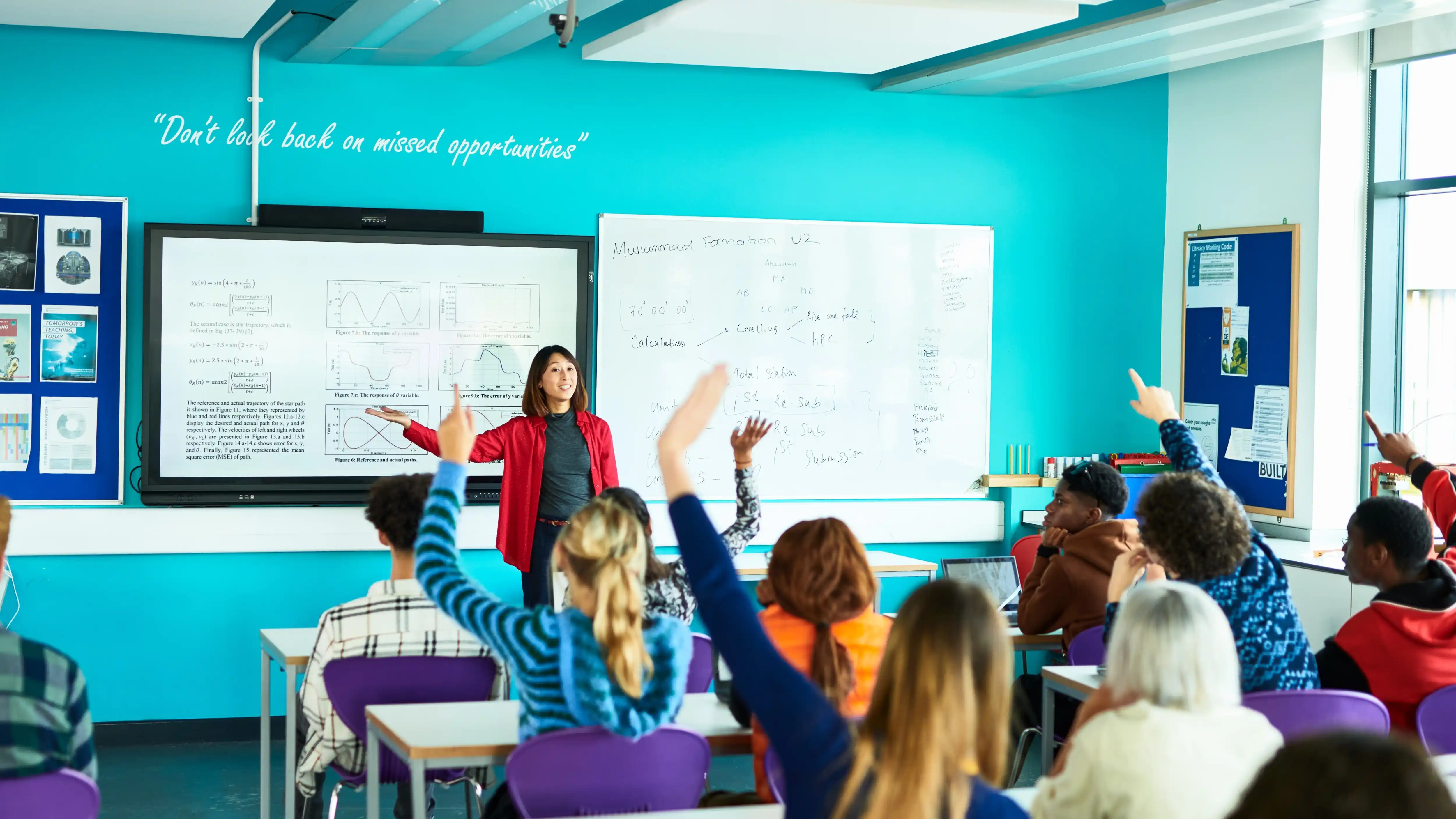
The foundation of Estonia’s curriculum success lies in its emphasis on student centered learning and competency based education. Rather than focusing solely on rote memorization or standardized testing, Estonia’s curriculum prioritizes developing critical thinking skills, creativity, and problem solving abilities. This approach is designed to equip students not just with knowledge but with the capacity to apply it flexibly in diverse contexts. For example, from early grades, students engage in project based learning that integrates multiple subjects, encouraging them to explore real world problems collaboratively. This shift away from traditional didactic teaching methods has been instrumental in motivating students and fostering deeper understanding.
A key aspect of Estonia’s curriculum reform has been its commitment to inclusivity and equity. The country has worked hard to ensure that all students, regardless of socio economic background or regional differences, have access to quality education and equal opportunities to succeed. The curriculum includes support mechanisms for students with special educational needs and those from minority communities, including language support for Russian speaking pupils. By embedding these supports directly into the curriculum framework, Estonia minimizes disparities and promotes social cohesion. The result is a more balanced system where achievement gaps have narrowed significantly, contributing to overall national progress.
Another pillar of Estonia’s curriculum success is the integration of digital technology and modern tools in teaching and learning processes. Estonia is widely recognized as one of the most digitally advanced societies globally, and this digital literacy permeates its education system. The curriculum explicitly incorporates ICT (Information and Communication Technology) competencies from an early age, ensuring that students develop essential skills for the digital era. Interactive digital platforms, e textbooks, and online assessment tools enhance engagement and personalize learning experiences. Importantly, teachers receive ongoing professional development to effectively integrate technology, making Estonia a pioneer in blending digital innovation with sound pedagogical principles.
Teacher professionalism and autonomy are fundamental to the effective implementation of Estonia’s curriculum. The country invests heavily in teacher education, recruitment, and continuous training, recognizing that teachers are the primary agents of educational change. Estonian teachers are well prepared to design lessons that align with curriculum goals, assess student progress qualitatively, and adapt instruction to meet individual needs. Moreover, the curriculum framework provides flexibility, allowing teachers to tailor content and methodologies to their classroom realities while maintaining national standards. This balance between guidance and autonomy fosters a motivated and skilled teaching workforce that drives student success.
Estonia’s curriculum is also characterized by a strong focus on transversal skills, often called 21st century skills, such as communication, collaboration, cultural awareness, and ethical responsibility. These skills are integrated across subject areas and grade levels, reflecting the recognition that knowledge alone is insufficient for navigating today’s complex societies. Citizenship education, environmental awareness, and entrepreneurship are woven into the curriculum, preparing students to participate actively and responsibly in their communities and economies. This holistic vision contributes to the development of well rounded individuals who are adaptable and socially conscious.
The governance and continuous improvement mechanisms supporting Estonia’s curriculum success are equally notable. The national curriculum is periodically reviewed through collaborative processes involving educators, policymakers, researchers, and community stakeholders. Feedback loops and evidence based evaluation ensure that the curriculum remains relevant, responsive to emerging trends, and aligned with international benchmarks. Estonia’s participation in global assessments, such as PISA, provides data that inform curricular adjustments and pedagogical strategies. This dynamic approach prevents stagnation and encourages innovation, enabling the system to anticipate and respond to future educational challenges.
In conclusion, Estonia’s curriculum success is a testament to the power of visionary policymaking combined with practical implementation strategies. By emphasizing competency based learning, equity, digital integration, teacher professionalism, and holistic skill development, Estonia has created an education system that prepares students for the demands of the 21st century. The country’s willingness to continuously refine its curriculum based on data and collaboration ensures sustained progress. Estonia’s experience serves as an inspiring example for nations worldwide seeking to revitalize education and empower future generations through thoughtful curriculum design.